Numerical Simulations of Transverse Compression in Wood
By: John A. Nairn
Introduction
A paper titled "Numerical Simulation of Transverse Compression in Wood," (by John A. Nairn, 2005) describes numerical simulations of realistic wood structures loaded in transverse compression. The numerical simulations used the material point method (MPM). This web site has QuickTime movies of the simulation results that could not be included in the paper.
Organization
Numerical simulations were run on loblolly pine, yellow poplar, and ponderosa pine. For loblolly pine and yellow poplar, simulations were run for both radial loading and tangential loading. For ponderosa pine, only tangential loading was simulated. Each of these five simulations are presented below with the following results:
- Model Images: MPM simulations were done by digitization of actual photographs of wood. The pixels in the digital images were mapped to material points in the MPM model. Each simulation shows the original digital image together with the MPM model for the simulation.
- Image Movie: These movies simply show the structure of the wood during compression and densification. The computer output was colored to match the initial wood micrograph as closely as possible.
- Plastic Energy Movie: The cell wall material was modeled as an elastic-plastic material. The color in these movies represent total plastic energy dissipation with blue being zero to red and lighter colors indicating high plastic energy. The onset of red zones indicates the onset of plastic collapse in the cell wall material.
- Load Baring Paths Movie: The color in these movies represent axial stress in the loading direction (x-direction stress for radial loading or y-direction stresses for tangential loading). Red indicates higher compressive stress while green and lighter colors are low stress.
Click the links to see each movie. After each movie, click the browser back button to return to this page. Note that the color movies begin with a frame in the initial condition that is not colored. The colors described above appear starting in the second frame.
Loblolly Pine
Model Images |
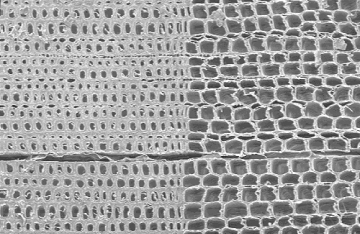
SEM micrograph of mature loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) taken from Ref. [1]. The specimen covers an area of 0.832 x 0.541 mm
|

MPM model of loblolly pine digitized from the SEM image.
|
Radial Loading
- Image Movie: Click to see movie.
- Plastic Energy Movie Click to see movie. Notice the plastic collapse occurs first in the early wood. At high strains the late wood yields. Everything has yielded at the highest strains.
- Load Baring Paths Movie Click to see movie. Notice the load baring paths along files of cell walls that line up with the loading direction.
|
Tangential Loading
- Image Movie: Click to see movie.
- Plastic Energy Movie Click to see movie. Notice the plastic collapse now occurs simultaneously in both late wood and early wood zones. Everything has yielded at the highest strains.
- Load Baring Paths Movie Click to see movie. Notice that most of the load is bared by the late wood zone.
|
Yellow Poplar
Model Images |
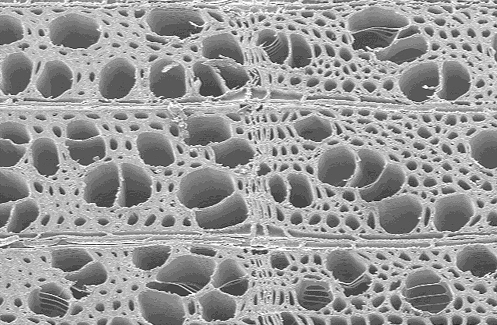
SEM micrograph of mature yellow poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera) taken from Ref. [1]. The specimen covers an area of 0.802 x 0.524 mm
|
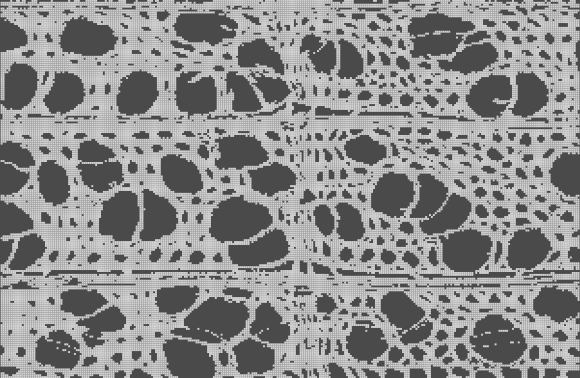
MPM model of yellow poplar digitized from the SEM image.
|
Radial Loading
- Image Movie: Click to see movie.
- Plastic Energy Movie Click to see movie. Notice the diffuse plastic collapse in regions baring the highest loads.
- Load Baring Paths Movie Click to see movie. Notice the load baring paths along the ray cells.
|
Tangential Loading
- Image Movie: Click to see movie.
- Plastic Energy Movie Click to see movie. Notice the diffuse plastic collapse in regions baring the highest loads.
- Load Baring Paths Movie Click to see movie. Loading baring baths are more diffuse in tangential loading than in radial loading
|
Ponderosa Pine
Model Images |
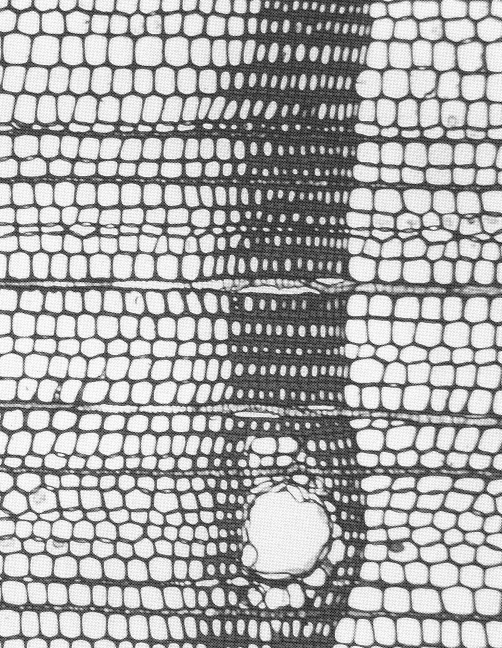
Optical micrograph of ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) taken from Ref. [2]. The specimen covers an area 1.00 x 1.29 mm
|
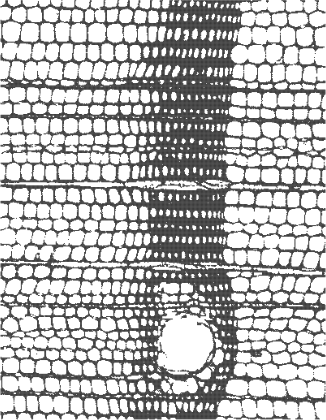
MPM model of ponderosa pine digitized from the Optical image.
|
| |
Tangential Loading
- Image Movie: Click to see movie.
- Plastic Energy Movie Click to see movie. Notice the plastic collapse in regions of high stress around the resin canal.
- Load Baring Paths Movie Click to see movie. Loading baring and buckling occurs in the late wood zone.
|
References
- Kultikova, E. V. 1999. "Structure and Properties Relationships of Densified Wood." M.S. Thesis, Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, USA.
- Haygreen, J. G. and J. L. Bowyer. 1996. Forest Products and Wood Science: An Introduction. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, USA.





